Table of Contents
Known in the industry as ‘fancy diamonds’, colored diamonds come in a range of shades. They’re much rarer than colorless diamonds and typically more valuable. In fact, the ratio of colored to colorless diamonds is 10,000:1.
What makes the color of a fancy diamond so fascinating is the perfect unity of science and beauty that lies at the heart of its creation.
How Are Colored Diamonds Formed?

All natural diamonds are made of carbon form over millions, or even billions of years, deep in the mantle of the earth under conditions of intense pressure and heat. They’re then brought to the surface of the earth through violent natural events, such as volcanic eruptions, from where they can be mined.
Synthetic diamonds (also called lab-created or manmade diamonds) are grown in labs, in environments that mimic natural conditions. These stones are identical to their natural counterparts – chemically, optically, and physically.
The technology required to create them is costly and labor-intensive. Synthetic colored diamonds often cost thousands of dollars but are much more affordable than natural colored diamonds.
How Does A Colored Diamond Get Its Color?
Diamonds are colored if a mutation or outside element is introduced during the formation phase. However, certain phenomena can also influence the color of the diamond.
Here are the active ingredients/phenomena responsible for the following diamond colors:
- Blue diamonds – Boron
- Grey diamonds – Hydrogen or boron
- Green diamonds – Natural radiation or hydrogen
- Yellow diamonds – Nitrogen
- Orange diamonds – Nitrogen and structural deformities
- Pink diamonds – Still unknown. Hue may be caused by possible deformation in atomic structure.
- Brown diamonds – Internal parallel grain lines
- Purple diamonds – Internal grain formation or hydrogen
- Red diamonds – Plastic deformation – atomic lattice is deformed
- Black diamonds – Graphite inclusions
A colored diamond is discovered only once in every ten thousand colorless diamonds. This makes colored diamond much more valuable than a colorless one.
How Are Fancy Colored Diamonds Evaluated?

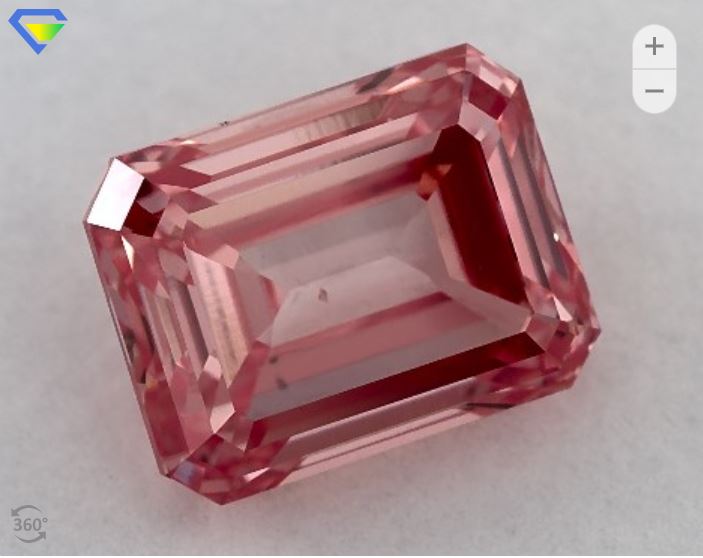
When evaluating a colored diamond, the four main criteria relate to the 4Cs – cut, color, clarity, and carat weight.
1. Color
The most important aspect of a fancy colored diamond is its color, which has a direct impact on the value of the stone.
According to the GIA, there are nine grades to categorize the color of fancy diamonds. These are:
Faint, Very Light, Light, Fancy Light, Fancy, Fancy Dark, Fancy Deep, Fancy Intense, Fancy Vivid
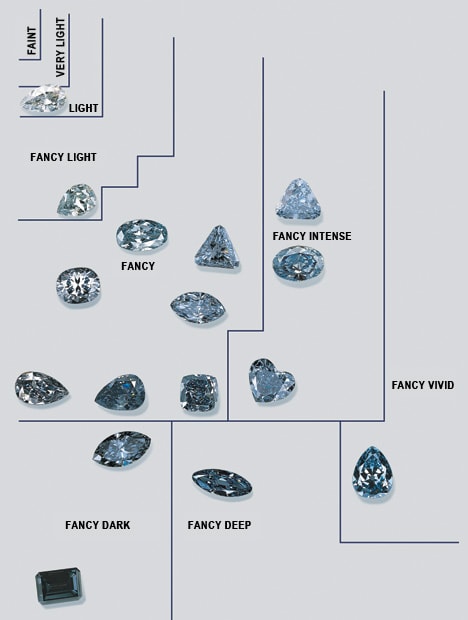
In general, colored diamonds with high saturation, medium to dark tones, and vivid color are considered more valuable.
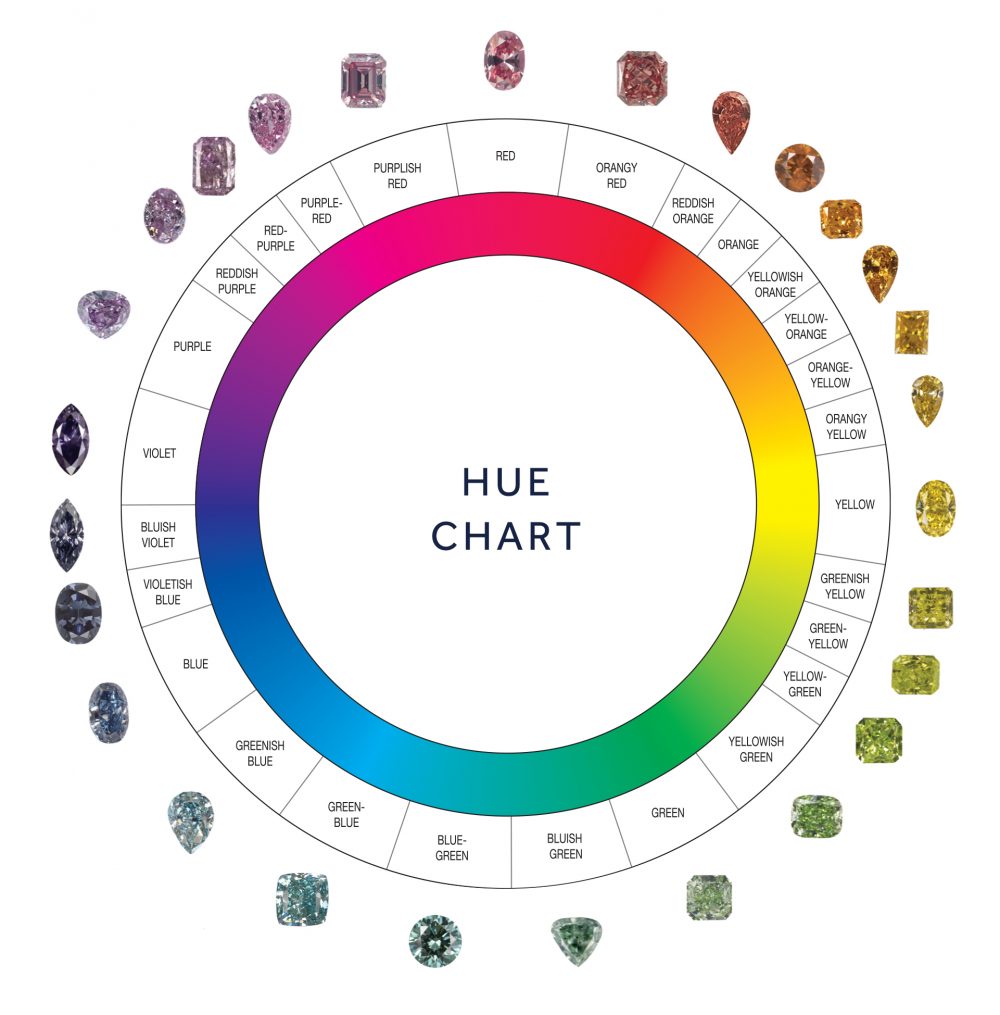
Hue
Hue refers to the colors that the diamond exhibits. The primary hue is the dominant color of the stone, while secondary hues refer to any additional colors.
A yellow diamond may have secondary tones of brown, orange, or green, while a green diamond may have flecks of grey and brown.
Pure colored diamonds are always more valuable than stones with other hues.
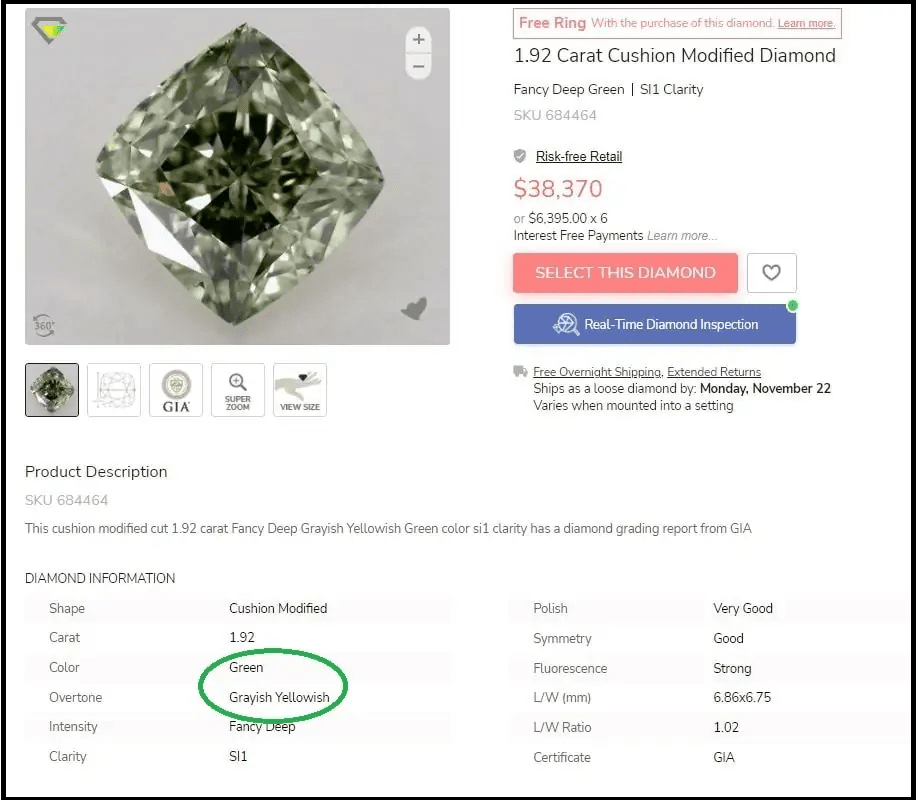
Fancy colored diamonds are described by the hues they exhibit. For example, a green diamond with grey hues may be called a Fancy Greenish Grey.
The overall color must be listed first, along with the secondary color/s to ensure transparency in the description.
Tone
The tone refers to how light or dark the diamond appears, and is affected by how much light is absorbed by the stone. There can be a wide variety of tones – from very light to almost black.
Colored diamonds often have descriptions such as Light Yellowish Orange – the word light in this example refers to the tone. Some other modifiers are very light, dark, and deep. Generally, darker tones are more valued.
Saturation
Saturation refers to how intense the color of the stone appears, and how evenly the color has spread throughout the stone.
This is where color diamonds will get the most amount of scrutiny when being appraised and where the true value of the diamond will be realised.
2. Clarity
Clarity refers to how clear the diamond appears. It’s evaluated by identifying inclusions the diamond may have.
For colored diamonds, clarity is the least important of the 4Cs. This is because most flaws in a fancy diamond are hidden by the color of the stone and therefore undetectable by the naked eye.
When it comes to rare colored diamonds, even though there may be heavy inclusions, these are overlooked in favor of the color.
3. Cut
With colorless diamonds, the cut is the most important factor as it brings out the stone’s brilliance and sparkle. However, when it comes to colored diamonds, even the cut is used to enhance the color of the stone.
It is typical for colored diamonds to be cut into fancy shapes, such as radiant, cushion, heart, pear, and marquise. Radiant and cushion cuts are generally favored as they bring in the most light and bring out most of the natural color of the stone. While pear and oval cuts are excellent choices as they tend to bring out the color beautifully, they can also be expensive choices.
You will find that the round brilliant shape is not a common cut for fancy diamonds, as it does not achieve the best color of the stone.
3. Carat
The carat weight of a diamond impacts its size and price. Type 1 diamonds (discussed below) are less expensive than Type 2 diamonds, which means that you can find them in many sizes. They’re also easily available and the price doesn’t hike up depending on the size.
Type 2 diamonds, such as pink and red, are exceedingly rare in large sizes. Even small stones can command hefty prices.
What are Synthetic and Enhanced Colored Diamonds?

Synthetic and enhanced diamonds are two excellent solutions to the dire shortage of colored diamonds.
Synthetic colored diamonds are grown in labs and can be much more affordable than naturally occurring diamonds. They’re also more sustainable and have a much lower impact on the earth than their mined counterparts.
Enhanced diamonds are colorless diamonds that have undergone treatment, such as irradiation, which then gives it a permanent hue. Many of the fancy diamonds on the market are in fact enhanced or lab grown. This fact is generally stated on the grading report.
What are Type 1 and 2 Diamonds?

Diamond types are a way of scientifically classifying diamonds based on chemical and physical properties. The common varieties of colored diamonds fall into Type 1, while the rarer and more valuable colors are Type 2.
Type 1 Diamonds
Type I diamonds are defined by the intake of nitrogen and blue light during the formation phase. These tones tend to give off a yellowish tone and represent around 98 percent of all diamonds mined. Brown, yellow, and orange diamonds fall under this category.
If the nitrogen is evenly spread out, the color will be deeply saturated. With deeper saturation the result would be colors such as canary orange or a deep yellow.
Type 2 Diamonds
Type II category of colored diamonds include hues that are much rarer and highly sought after, such as colorless, blue, red, pink and green diamonds.
Type II diamonds are determined by the lack of nitrogen during the diamond’s creation. These stones represent about 1 to 2 percent of all diamonds mined.
Famous Fancy Colored Diamonds
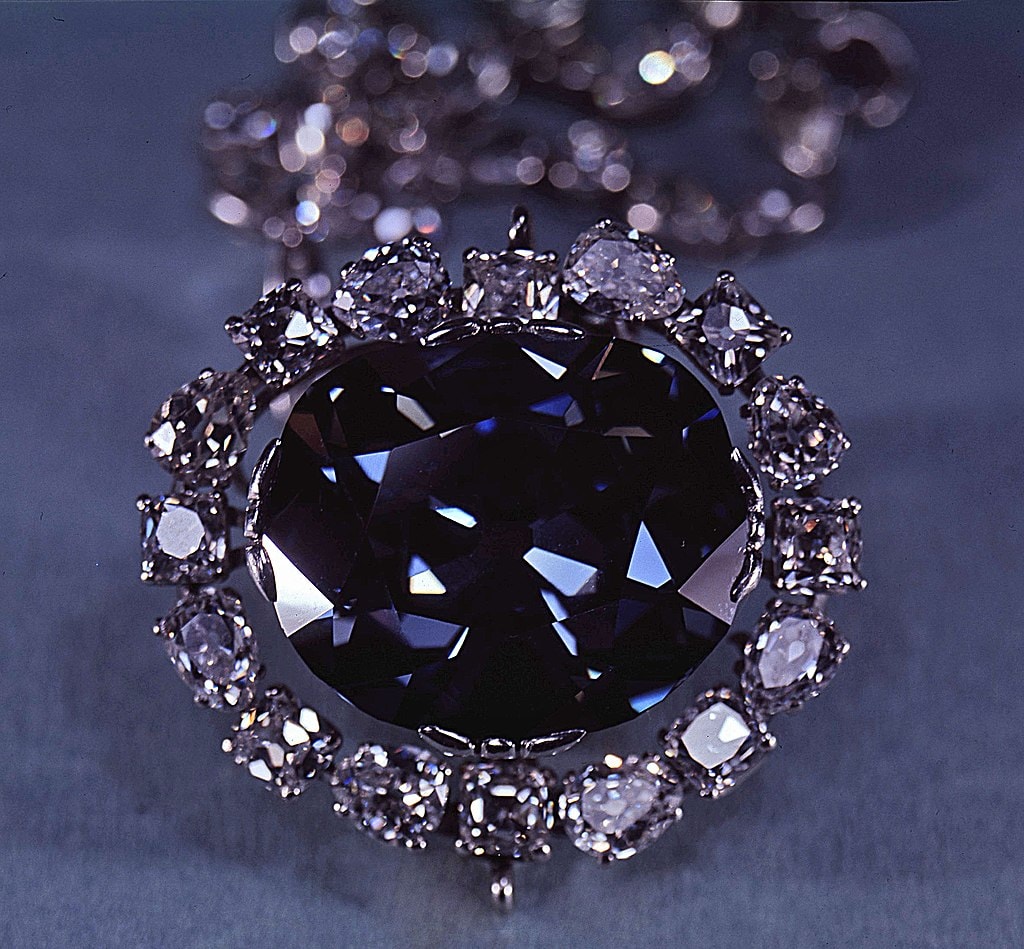

Colored diamonds have fascinated humans for centuries and have always been valued and coveted. Some of the most famous colored diamonds have gone on to become iconic objects, with stories that captivate even today.
- Blue: Probably the most famous of is the stunning dark blue Hope Diamond, which now resides in the Smithsonian Museum in Washington D.C.
- Pink: Another rare diamond to make history and one of the oldest in the world is the pink “Darya-i-Nur” or Ocean of Light and is a whopping 182 carats. Very few diamonds are discovered in such a shade let alone impressive size. This light pink diamond remains part of the Iranian Crown Jewels.
- Brown: The Golden Jubilee diamond is the largest cut and faceted diamond. It weighs an incredible 545.67 carats. De Beers hired famed diamond cutter Tolkowsky to cut the diamond, a task which took two years to complete. This cushion cut brown diamond is said to be worth about $12 million.
- Red: The Rob Red, named after its owner Robert Bogel, is a small stone at .59 carats, featuring a pear shape. What makes this stone so special is that it’s the only graded red diamond in the world with the most saturation and purest red hue.
- Green: Weighing about 41 carats, the Dresden Green is the biggest known natural green diamond ever to have been discovered. This continues to be the largest natural green diamond. What makes it stand out is that it has perfect saturation, with the green hues equally spread within the stone.
Where to Buy Colored Diamonds
Colored diamonds are highly valuable and a major purchase – so it’s essential to put in careful thought prior to purchasing. If you’re buying online, always ensure that the retailer has a proven track record, is able to provide you necessary information you require about the diamond, including a lab report from a reputable lab like the GIA.
We recommend the following retailers when purchasing colored diamonds:
- James Allen: James Allen ranks among the best in online diamond sales. With a wide range of natural and synthetic colored diamonds at reasonable prices, James Allen streamlines online shopping with their groundbreaking Diamond Display Technology. They also have a Diamond Expert on hand to assist you with the purchasing process.
- Blue Nile: A leader in online diamond retailing, Blue Nile also offers a good selection of loose colored diamonds, and a small but expertly crafted selection of colored diamond jewelry as well as lab created diamond jewelry. They’re continuously improving their image and video quality, and have excellent after sales policies and customer service.
- Brilliant Earth: You can find lab created colored diamonds and jewelry at Brilliant Earth, a retailer known for their commitment to ethically sourced gemstones and jewelry. Talk to one of their friendly reps who will walk you through the purchasing process.
Wrapping Up
Colored diamonds are among the most coveted of all gemstone types. They get their colors by the unique conditions that exist as they’re formed in the ground. However, today, you can also find high-quality synthetic versions that offer the same benefits as mined colored diamonds, but at much lower costs.










